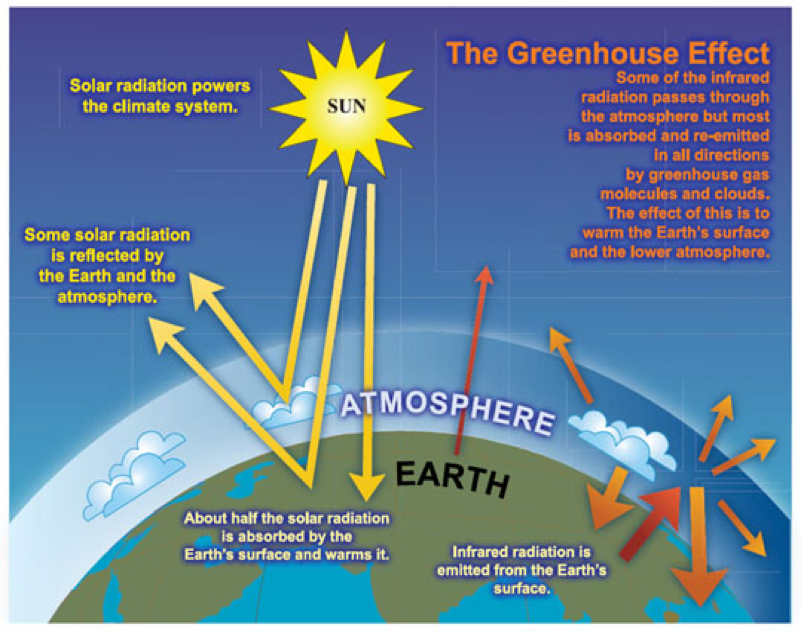
The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some of this energy (as infrared, or Greenhouse gas definition Greenhouse gases are the gases which are responsible for causing the greenhouse effect Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examples Deforestation and Greenhouse Gases Report Human activities produce large amounts of greenhouse gases (GHGs), primarily carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), and thus contribute to global warming The use of fossil fuels is the primary source of CO 2 emissions, but the removal of trees from forested land has also contributed

Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
Greenhouse gases definition and examples
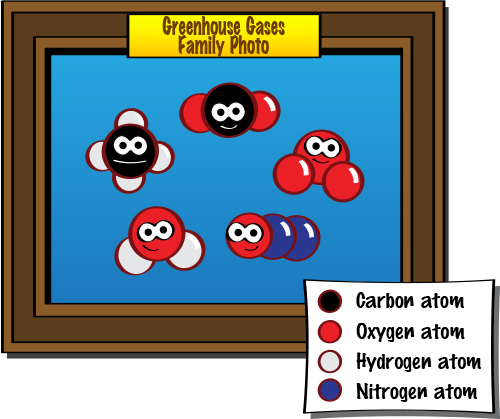
Greenhouse gases definition and examples-Although greenhouse gases make up only about 1 percent of the Earth's atmosphere, they regulate our climate by trapping heat and holding it in a kind of warmair blanket that surrounds the planetSome greenhouse gases occur naturally and enter the atmosphere as a result of both natural processes (such as decomposition of organic matter) and human activity (such as burning fossil fuels and agriculture) Greenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse
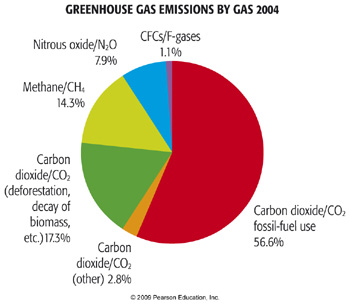



Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming
Greenhouse effect Some thermal energy from the Earth's surface escapes into space If too much thermal energy escaped, the planet would be very cold However some gases in the atmosphereWord forms (plural) greenhouse gases noun ( Extractive engineering General) A greenhouse gas is a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation in the atmosphere Carbon dioxide is considered to be a greenhouse gas because it traps heat radiated into the atmosphere Carbon dioxide is widely considered to be Greenhouse effect definition is warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to
Burning these materials releases what are called greenhouse gases into Earth's atmosphere There, these gases trap heat from the sun's rays inside the atmosphere causing Earth's average temperature to rise This rise in the planet's temperature is called global warming The warming of the planet impacts local and regional climates Throughout Earth's history, The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effectMost greenhouse gases are natural water vapor is the most common, and causes most of the greenhouse effect on Earth Other greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbon and ozone Without greenhouse gases, life as we know it would probably not be possible on Earth, because heat is important for life Natural emissions of greenhouse gases vary For example
The warming effect of the greenhouse gases is expected to take place everywhere, but the cooling effect of the pollution aerosols will be somewhat regionally dependent, near and downwind of industrial areas No one knows what the outcome will be of atmospheric warming in some regions and cooling in others Climate models are still too primitive to provide reliable insight into theGreenhouse gases are a hot topic (pun intended) when it comes to global warming These gases absorb heat energy emitted from Earth's surface and reradiate it back to the ground In this way, they contribute to the greenhouse effect, which keeps the planet from losing all of its heat from the surface at night The concentrations of various greenhouse gases in the atmosphereGreenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming one



Greenhouse Gas Reduction




What Is A Carbon Footprint Definition Of Carbon Footprint
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activitiesIn 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals) A carbon footprint is defined as the total amount of greenhouse gases produced to directly and indirectly support human activities, usually expressed in equivalent tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) In other words When you drive a car, the engine burns fuel which creates a certain amount of CO2, depending on its fuel consumption and the driving distanceFluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6 Once emitted into the atmosphere, they disperse widely around the globe;



1




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
Greenhouse gas definition is any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect How to use greenhouse gas in a sentenceOf the six greenhouse gases, three are of primary concern because they're closely associated with human activities Carbon dioxide is the main contributor to climate change, especially through the burning of fossil fuels Methane is produced naturally when vegetation is burned, digested or rotted without oxygen Oil and gas production, cattle farming, waste dumps and rice farming release This is called the greenhouse effect, and the molecules that trap the heat are called greenhouse gases Even though greenhouse gases don't make a hard surface like the glass of a greenhouse, but because they have a similar effect in keeping our planet warm, the term "Greenhouse Effect" is a good description The greenhouse effect keeps the temperatures on




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



Simple
Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedFluorinated gases (Fgases) are manmade gases that can stay in the atmosphere for centuries and contribute to a global greenhouse effectThere are four types hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) and nitrogen trifluoride (NF 3)Fgases are a subgroup of the halogenated gases, the majority of which are halocarbons that include fluorine,Greenhouse gas definition 1 a gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2 a gas that causes the Learn more




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Topic 5 By Melody F
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into space This keeps the Earth warmer than it would be without these gases Greenhouse gases are not a Greenhouse gas emissions and atmospheric concentrations have increased over the past 150 years Emissions of several important greenhouse gases that result from human activity have increased substantially since largescale industrialization began in the mid1800s Most of these humancaused (anthropogenic) greenhouse gas emissions were carbon dioxide (CO2)The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action — through activities such as industry, intensive agriculture and livestock farming,




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




The Greenhouse Effect Explained
Changes in farming practices could also reduce greenhouse gas emissions For example, farms use large amounts of nitrogenbased fertilizers, which increase nitrogen oxide emissions from the soil Reducing the use of these fertilizers would reduce the amount of this greenhouse gas in the atmosphere The way farmers handle animal manure can also have an effect on global warming In 19, greenhouse gas emissions from transportation accounted for about 29 percent of total US greenhouse gas emissions, making it the largest contributor of US greenhouse gas emissions In terms of the overall trend, from 1990 to 19, total transportation emissions have increased due, in large part, to increased demand for travel The number ofExamples of greenhouse gas in a sentence, how to use it 98 examples In addition, there has been increased interest in the role of agricultural




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



The Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight But unlike those gases, greenhouse gases are not transparent to outgoing heat (longwave infrared radiation), which radiates from the sunwarmed surface of Earth day and night Some heat escapes freely to space, but some is absorbed by greenhouse gasThey are removed from the




American English At State Do You Know About The Greenhouse Effect Learn About It With This Americanenglish Graphic What Can We Do To Reduce Greenhouse Gases Facebook




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist Sources of greenhouse gases Some greenhouse gases, such as methane, are produced through agricultural practices, in the form of livestock manure, for example Others, like CO2, largely resultGreenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gases




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Infographic Europe Needs A Definition Of Carbon Dioxide Removal Zero Emissions Platform



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Meet The 10 Worst Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gases Environmental Chemistry Archaeology News




Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Weatherquestions Com Everyday Examples Of The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
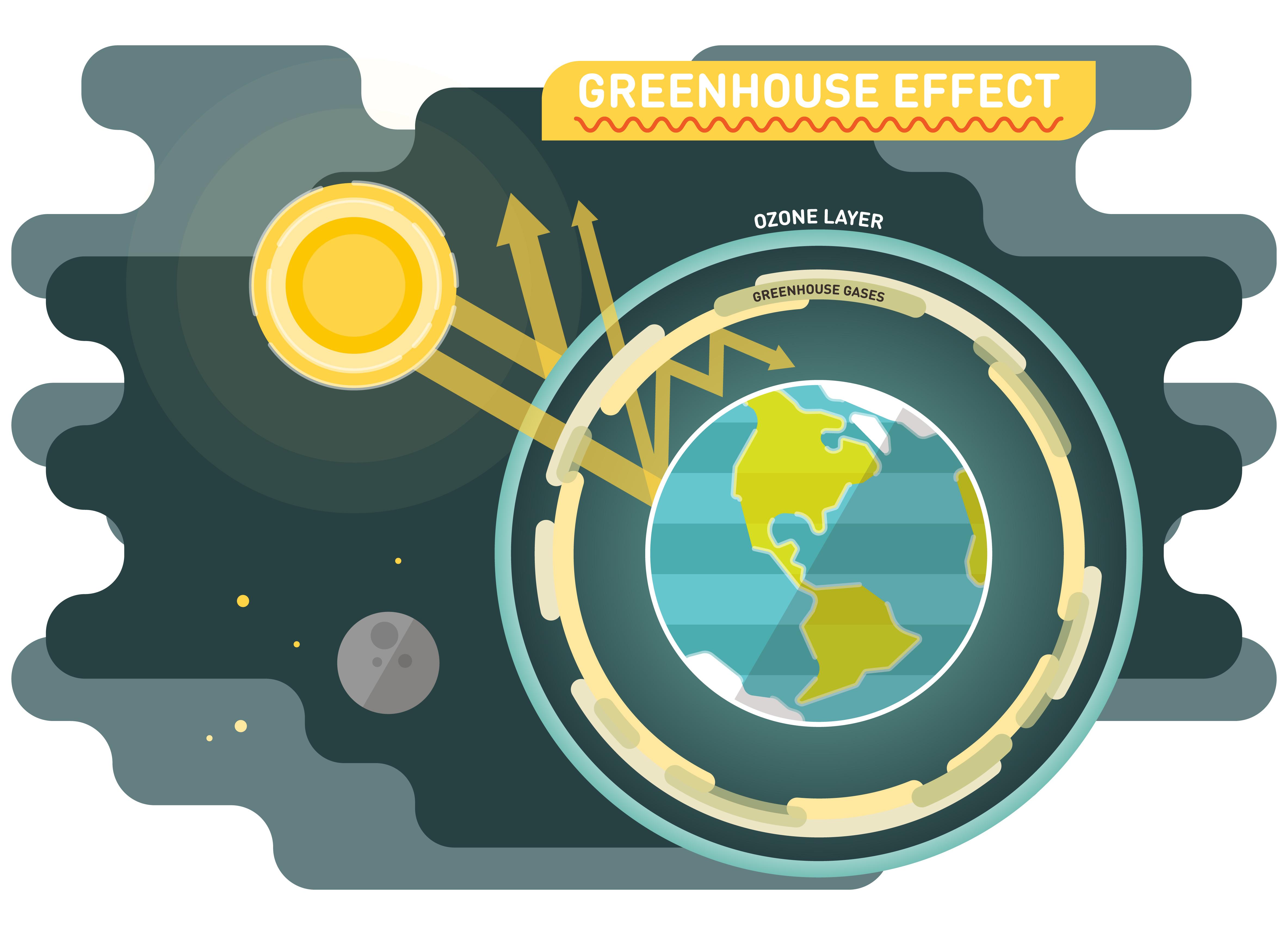



Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate



1




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Revised Papers Due April 17 N Strunk And



Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy




Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming




Measuring Urban Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Challenge Of Comparability




Pcf World Forum Executive Summary 1 Product Carbon Footprint Pcf By Thema1 Accelerating Social Change Issuu




Pdf Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases And Their Impact On Global Warming
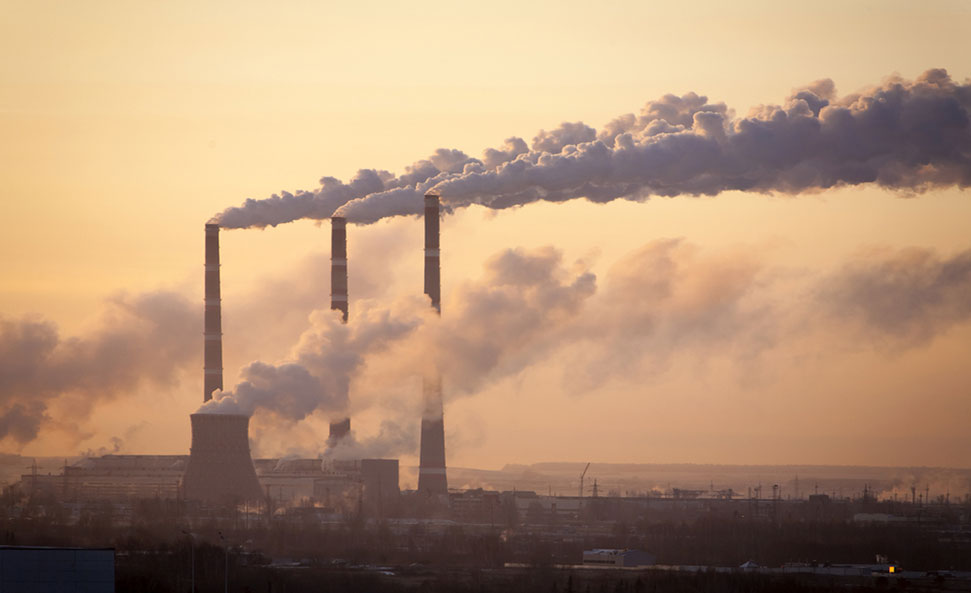




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases Overview Examples What Are Greenhouse Gases Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science



Environment For Kids Global Warming




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases



Economic Approaches To Greenhouse Warming




Sources And Sinks American Chemical Society




Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Samsung




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
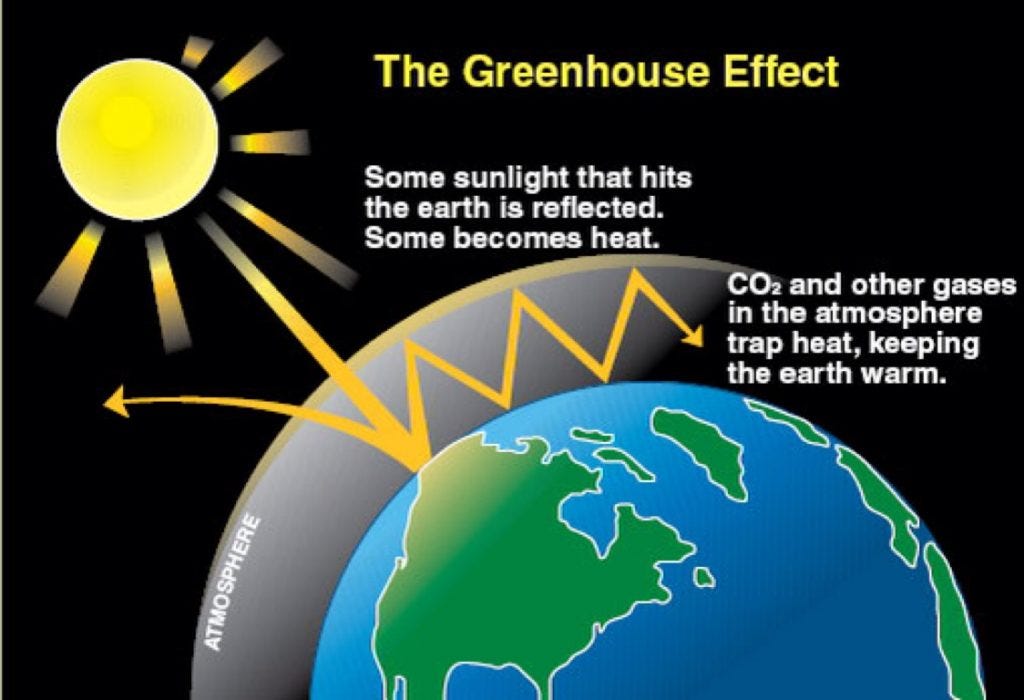



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Greenhouse Gases At Epa Us Epa
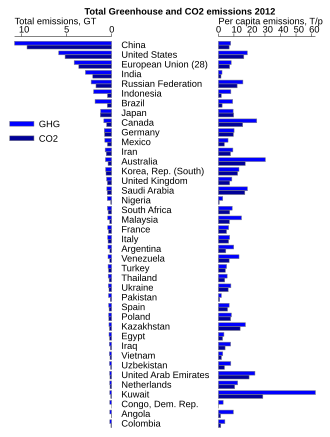



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gasses




Glossary Ipcc Task Force On National Greenhouse Gas Inventories



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Climate Change Project Ll Part 2 स ट र ब र ड द व र d47



What Does Greenhouse Gases Mean Definition Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gases Stands For Carbon Dioxide And Other Gaseous Emissions Resulting From Human Activity That Cause Heat To Be Trapped In




Mean Machines Greenhouses Define The Terms 1 Greenhouse Gas A Gas That Contributes To The Greenhouse Effect By Absorbing Infrared Radiation Carbon Dioxide Ppt Download




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Iso 1 18 En Greenhouse Gases Part 1 Specification With Guidance At The Organization Level For Quantification And Reporting Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Removals




Greenhouse Gases Overview Examples What Are Greenhouse Gases Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



You Too Can Master Value Chain Emissions Greenhouse Gas Protocol



Untitled Document




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Natural Sources Of Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere




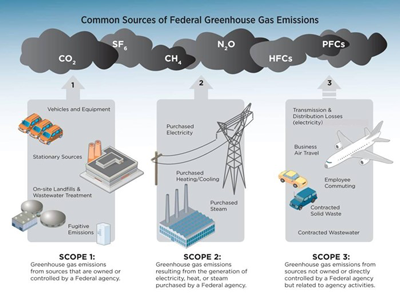
What Are Scope 1 2 3 Emissions Anthesis
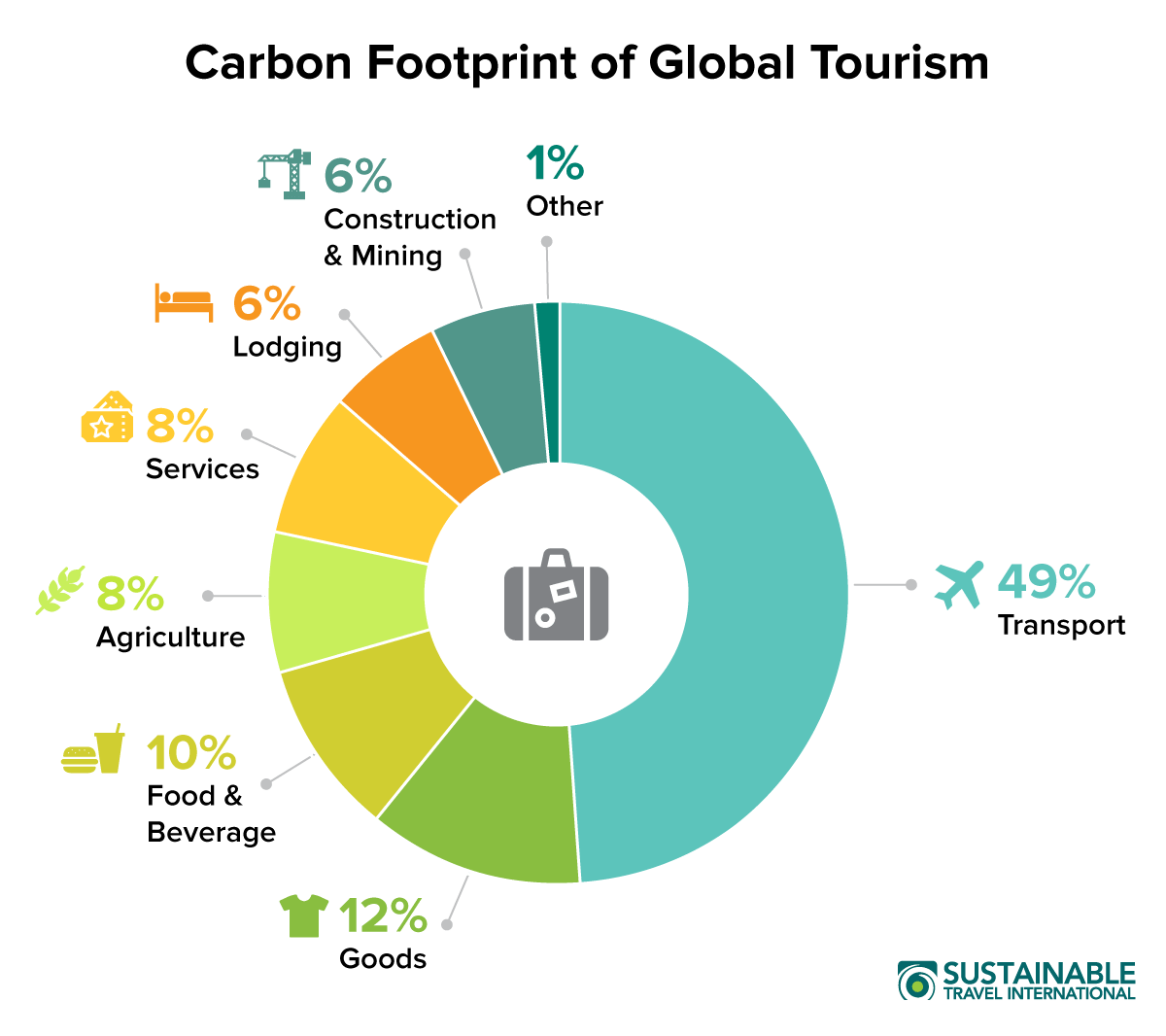



Carbon Footprint Of Tourism Sustainable Travel International




Greenhouse Definition For English Language Learners From Merriam Webster S Learner S Dictionary English Language Learners Greenhouse Earth Atmosphere




Greenhouse Gas Ghg Meaning And Several Examples



Natural Sources Of Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Greenhouse Gas Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
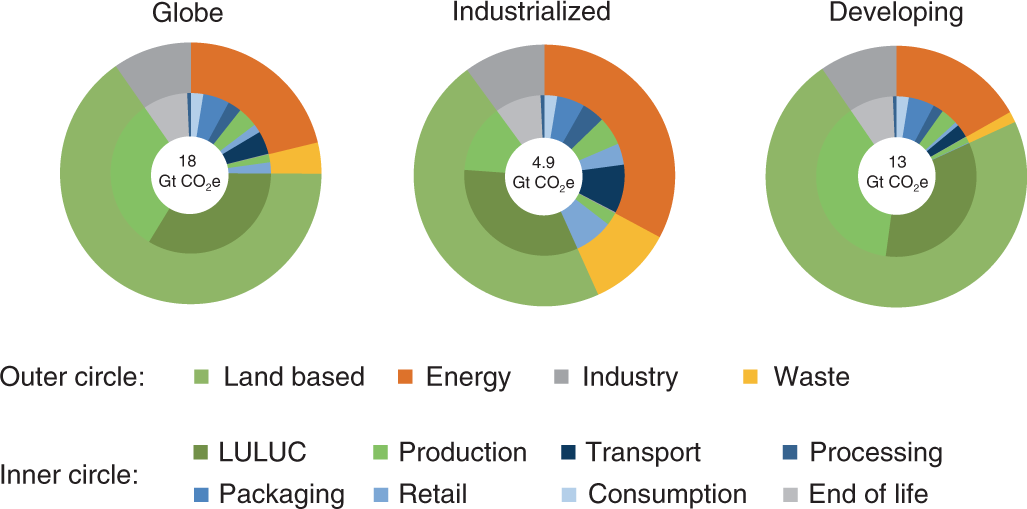



Food Systems Are Responsible For A Third Of Global Anthropogenic Ghg Emissions Nature Food
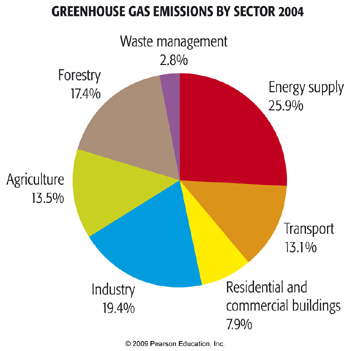



Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gas Emissions Meteo 469 From Meteorology To Mitigation Understanding Global Warming



Meet The Greenhouse Gases Nasa Climate Kids




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
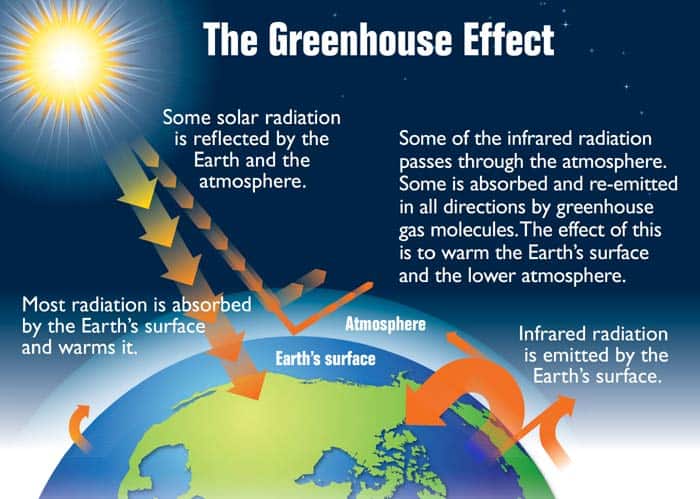



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
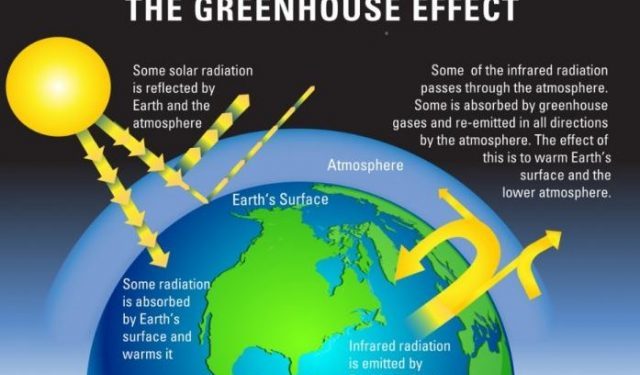



Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Definition Causes And Impact




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Difference Between Complete Combustion And Incomplete Combustion Definition Properties Examples Exothermic Reaction Greenhouse Gases Molecular




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
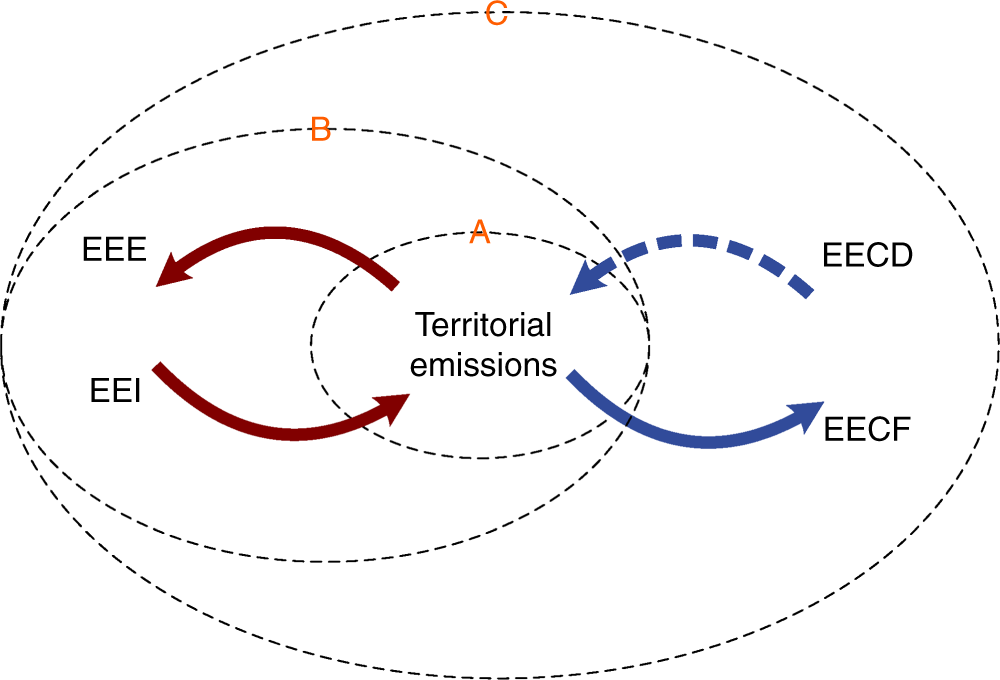



Consumption Based Greenhouse Gas Emissions Accounting With Capital Stock Change Highlights Dynamics Of Fast Developing Countries Nature Communications
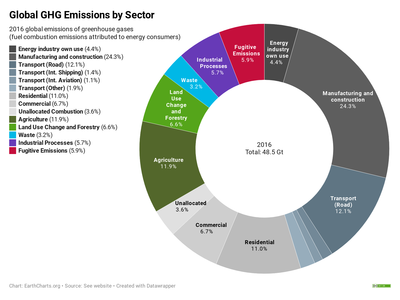



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems
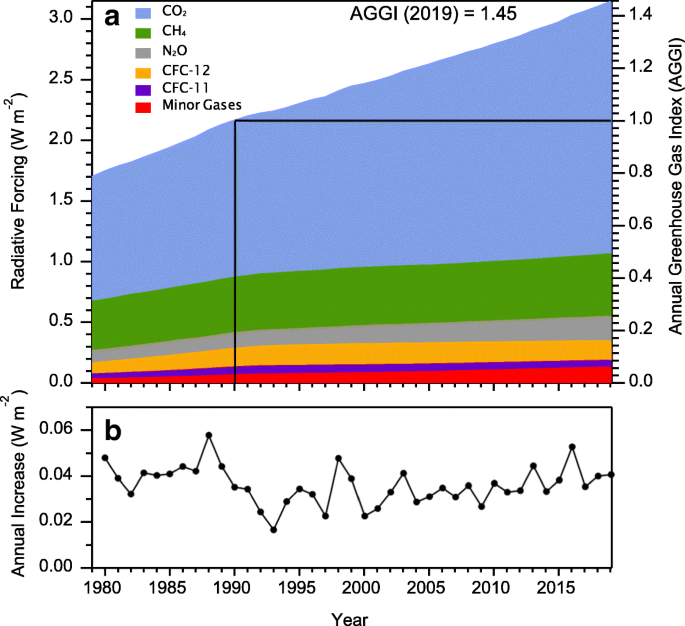



Observations Of Greenhouse Gases As Climate Indicators Springerlink




What Is The Kyoto Protocol Definition Summary Pros Cons Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Iso 2 19 En Greenhouse Gases Part 2 Specification With Guidance At The Project Level For Quantification Monitoring And Reporting Of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions Or Removal Enhancements
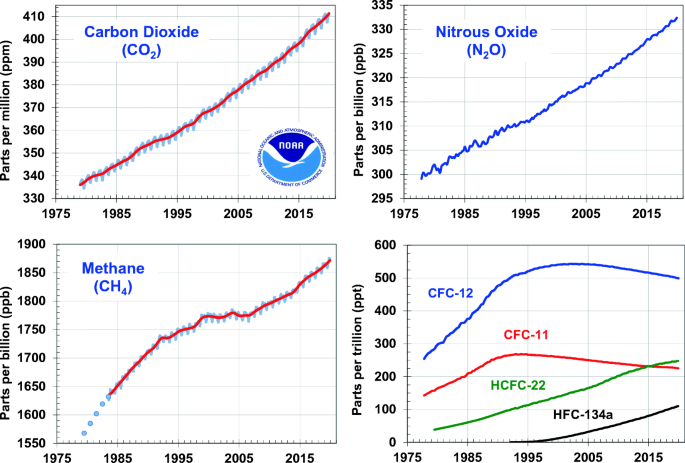



Observations Of Greenhouse Gases As Climate Indicators Springerlink




Insight Carbon Footprint Labelling A Growing Trend Among Consumer Goods Companies Icis
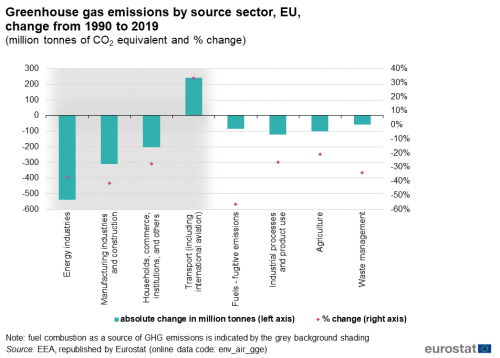



Climate Change Driving Forces Statistics Explained



Ozone Layer
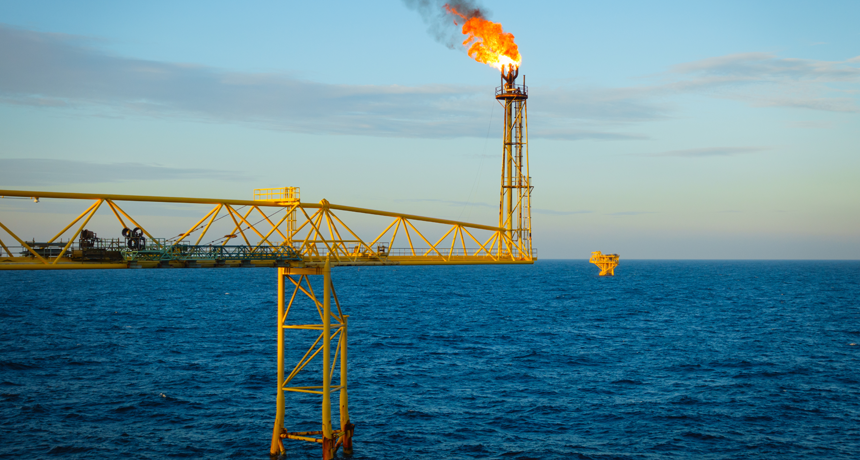




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students
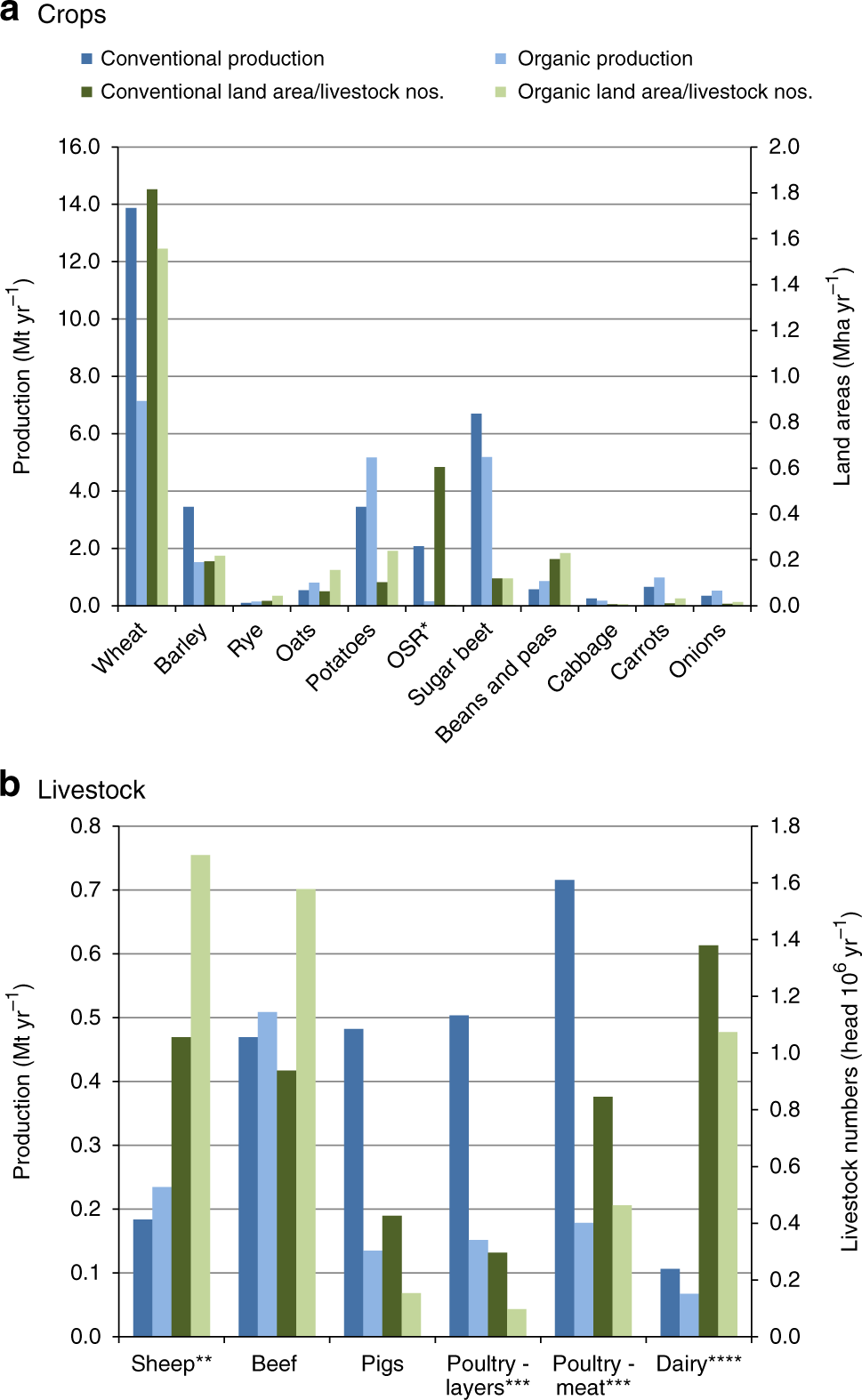



The Greenhouse Gas Impacts Of Converting Food Production In England And Wales To Organic Methods Nature Communications



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Iso 3 06 En Greenhouse Gases Part 3 Specification With Guidance For The Validation And Verification Of Greenhouse Gas Assertions




What Are Hydrofluorocarbons Eia Global
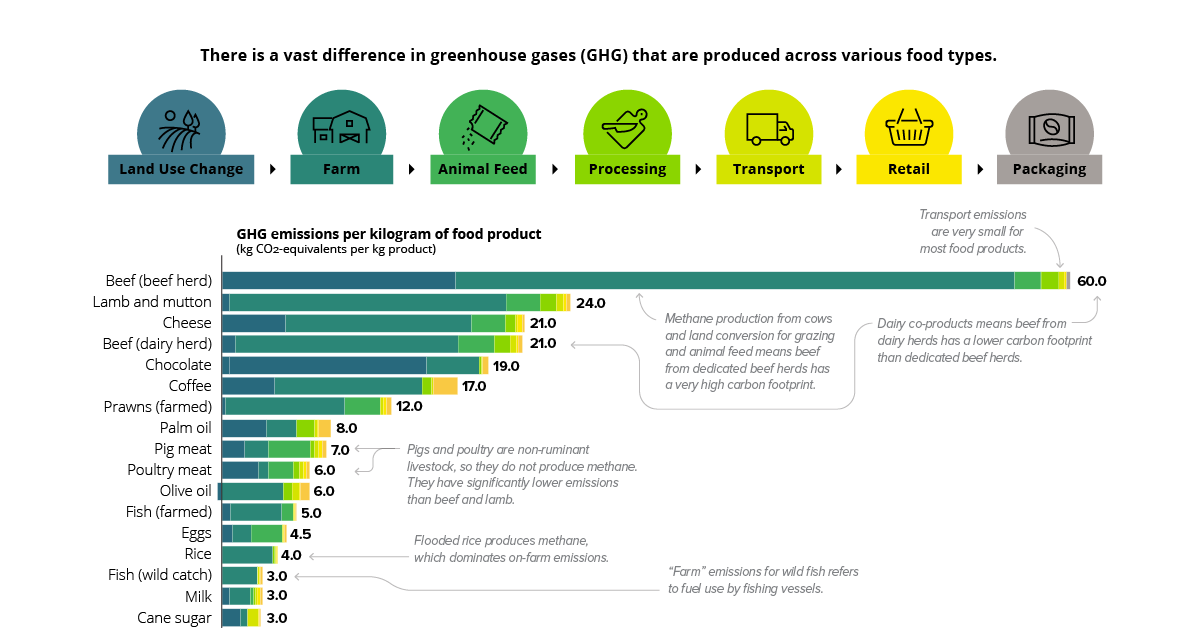



Chart The Carbon Footprint Of The Food Supply Chain




Climate Changes Symptoms And Prevention Adam Figiel Institute




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



Carbon Dioxide And Greenhouse Gases Storyboard


